Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a leading cause of blindness among working-age adults, affecting millions worldwide. The prevalence of DR is alarmingly high, affecting an estimated 34.6 million people globally. In the United States alone, it is estimated that 7.7 million adults have some form of diabetic retinopathy.
How Does Diabetes Affect the Eye?
Most of the damage occurs due to chronically elevated blood sugar. Firstly, high blood sugar damages the lining of blood vessels, making them less flexible and more prone to narrowing. This narrowing increases resistance to blood flow, leading to higher blood pressure.
Secondly, diabetes can affect the kidneys’ ability to regulate fluid and sodium balance in the body. When the kidneys don’t function optimally, excess fluid and sodium can build up, increasing blood volume and, consequently, blood pressure.
Thirdly, diabetes can damage the nervous system, disrupting blood pressure regulation and contributing to hypertension. This elevated blood pressure stresses weakened retinal blood vessels, increasing leakage and bleeding, causing macular swelling (diabetic macular edema) and distorted vision.
Furthermore, oxygen deprivation due to damaged blood vessels leads to retinal ischemia, causing cell death and impaired function. In advanced stages, new, fragile blood vessels (proliferative diabetic retinopathy or PDR) can form, leading to bleeding, scar tissue, and potential retinal detachment. Diabetes also directly affects retinal neurons, further impairing vision.
As you can see, the process is complex and occurs on multiple levels. Tragically, many people with DR experience vision loss or blindness due to late diagnosis and inadequate treatment. This is particularly concerning given that DR is largely preventable with early detection and proper management.
How Can Artificial Intelligence Solve the Problem?
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to revolutionize healthcare, including eye care. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, such as medical images, to identify patterns and make predictions that may be difficult for humans to discern, or that would take too much time, making mass screenings inefficient.
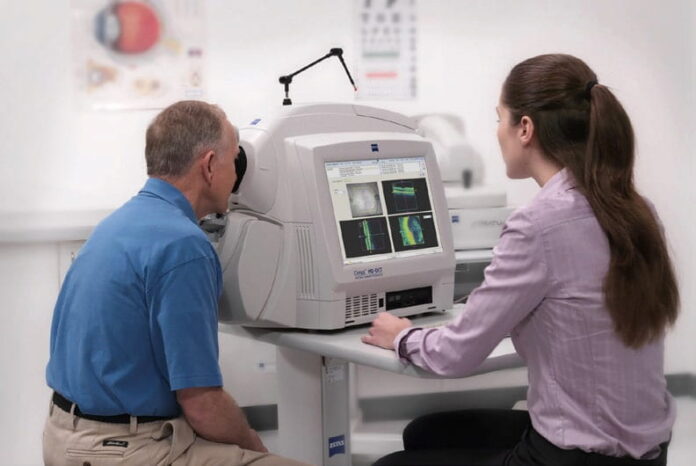
In the context of DR, the most promising applications involve optical coherence tomography (OCT) based AI-powered systems that can analyze retinal scans to detect the subtlest and earliest signs of the pathology before they become clinically visible.
AI algorithms can analyze these OCT scans to identify subtle changes in the retinal layers, such as thickening or fluid accumulation, which may indicate the presence of DR. They can provide quantitative analysis of DR biomarkers in terms of area and volume, enabling swift detection and localization of pathological changes with uncompromised accuracy.
The adoption of OCT AI for Diabetic Retinopathy screening significantly improves the early detection and management of the disease. Some AI-powered systems also offer color-coded visualization of every DR biomarker, optimizing clinical workflow and making it easier for clinicians to identify and track changes. Moreover, these systems enable progression analysis, objectively monitoring the results of DR treatment by comparing OCT examinations from different visits.
One of the significant advantages of AI in OCT analysis is its ability to standardize diagnostic accuracy. Variability in manual interpretation, often influenced by clinician experience and fatigue, can lead to missed or delayed diagnoses. AI models trained on vast datasets of OCT images can provide consistent, objective evaluations, reducing the risk of oversight. Moreover, these models can prioritize cases based on severity, enabling healthcare providers to address critical cases promptly.
The scalability of AI-powered OCT solutions also enhances accessibility to DR screening, especially in underserved regions. Remote screening programs can leverage AI to interpret OCT scans locally, eliminating the need for highly specialized ophthalmologists on-site. This not only improves early detection rates but also optimizes healthcare resources.
As AI technology continues to evolve, its role in OCT analysis for DR detection is set to expand further. Integrating these tools into routine screening programs can significantly reduce the global burden of DR and improve patient outcomes by enabling timely intervention and personalized care.
Did you find this helpful? Check out our other helpful articles on our website.
Read Also
- Automated Healthcare Software Solutions: How Intelligent Platforms Are Redefining Clinical, Administrative, and Operational ExcellenceThe healthcare industry is undergoing a seismic transformation. Rising patient volumes, value-based care models, staffing shortages, and complex regulatory demands have prompted organizations to look beyond traditional tools and embrace advanced software automation. As providers search for innovative partners capable of tailoring these sophisticated systems to real-world workflows, many turn to MCSI (Managed Care Systems,… Read more: Automated Healthcare Software Solutions: How Intelligent Platforms Are Redefining Clinical, Administrative, and Operational Excellence
- Why Whole Slide Imaging Shapes the Future of Digital PathologyWhole slide imaging has become one of the most important developments in modern pathology. It changes how tissue is examined, how cases are shared and how pathologists collaborate with the wider care team. More than a technological upgrade, it represents a shift in how laboratories think about their workflow, their storage needs and the tools… Read more: Why Whole Slide Imaging Shapes the Future of Digital Pathology
- Comparing 2025 Dental Practice Management Software OptionsSoftware Key Strengths Potential Limitations Best For Dentimax • Offers both cloud-based and on-premise/server deployment. • Tight integration between imaging (e.g. X-ray sensors) and practice management, charts, treatment planning, imaging all in one. • Transparent pricing and relatively simple UI/usability; solid for small to medium general practices. • May lack some of the… Read more: Comparing 2025 Dental Practice Management Software Options
- Top Innovations in Dermatology and Skincare TechnologiesHave you ever wondered how skincare keeps getting better year after year? From fighting acne to reducing wrinkles, today’s treatments seem more advanced than ever before. The tools and techniques used by dermatologists today are smarter, safer, and more effective than those we had just a few years ago. These breakthroughs don’t just help with… Read more: Top Innovations in Dermatology and Skincare Technologies
- Telehealth and Beyond: Building a Connected Continuum of CareHealthcare is on the verge of a radical transformation. Technology no longer simply supports medicine; it actively shapes how care is delivered and experienced. Achieving a seamless continuum demands more than deploying tools—it requires intentional design, coordinated teamwork, and innovative platforms that adapt to diverse clinical and patient needs. This article explores key strategies for… Read more: Telehealth and Beyond: Building a Connected Continuum of Care
- Optimizing CT Protocols: The Hidden Key to Efficiency and Cost Savings in RadiologyIntroduction: Why CT Protocol Optimization Matters Computed Tomography (CT) is a cornerstone of modern diagnostic imaging, providing critical information across nearly every medical specialty. However, maximizing the value of CT — both clinically and financially — requires more than just advanced hardware. The real secret lies in the optimization of CT protocols. When CT protocols… Read more: Optimizing CT Protocols: The Hidden Key to Efficiency and Cost Savings in Radiology
- The Role of Carbide Burs in Modern Dental ProceduresAs a result of this procedures need to be well coordinated and to this end, precision tools are used by dental practitioners. Among the most essential tools in a dentist’s arsenal are carbide burs, which have revolutionized various aspects of dental work. Today’s dentistry cannot work without these tools as they are both strong, sharp,… Read more: The Role of Carbide Burs in Modern Dental Procedures
- Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy: The AI AdvantageDiabetic retinopathy (DR) is a leading cause of blindness among working-age adults, affecting millions worldwide. The prevalence of DR is alarmingly high, affecting an estimated 34.6 million people globally. In the United States alone, it is estimated that 7.7 million adults have some form of diabetic retinopathy. How Does Diabetes Affect the Eye? Most of… Read more: Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy: The AI Advantage