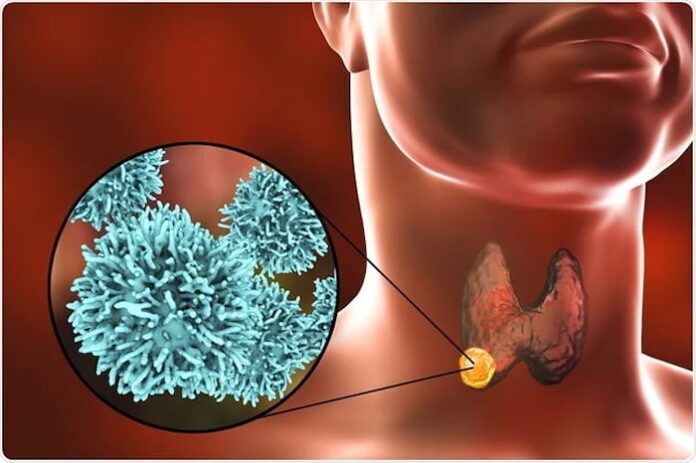
No matter the type, cancer sounds extremely frightening. Thyroid cancer, basically affects the thyroid gland cells and can become dangerous if it enters an aggressive stage of the disease.
Do not worry, though; thyroid cancer is among the most treatable types of cancer. There are some things you should be aware of.
Let’s start with the basics of thyroid cancer!
What is Thyroid Cancer?
According to studies from the American Cancer Society, thyroid cancer forms malignant (cancerous) lump cells that grow in the thyroid gland.
The thyroid gland is butterfly-shaped in front of the neck. It produces hormones and regulates metabolism, determining how your body uses energy.
The exact cause is often unknown, but when your thyroid is linked to inherited conditions or cells begin to change or mutate in DNA. As a result, cancerous cells grow and multiply uncontrollably, eventually forming a tumor.
There are several types of thyroid cancer that most thyroid doctors research may find, including:
– Approximately 80% of thyroid cancer cases are papillary thyroid cancer, making it the most prevalent type. It typically grows slowly and has a favorable diagnosis.
– Unlike papillary thyroid cancer, follicular thyroid cancer accounts for 10 to 15% of cases and is typically more aggressive.
– The thyroid’s C cells, which create the hormone calcitonin, are where Medullary Thyroid Cancer—a rarer form of the disease—begins. In some cases, it is hereditary.
– Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer is the most deadly and rare type of thyroid cancer. It spreads quickly and has a poor prognosis.
– Thyroid lymphoma is a rare kind of thyroid cancer that develops from immune system cells within the thyroid gland.
As you are aware, the exact cause of thyroid cancer is frequently unknown; however, certain risk factors, including radiation exposure, family history, particular genetic syndromes, and age, can raise the risk.
The Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer impairs the production of hormones, which disrupt metabolism and lower energy levels. Because thyroid cancer is a less common type of cancer than the others.
However, only in the United States it is estimated that 43,720 people have thyroid cancer, and 2,120 of them will pass away from it in 2023. Women are more likely than men to experience thyroid disorders, so this is not news. Even women’s hormonal effects tend to cause them to develop thyroid cancer three times more.
However, in its earliest stages, thyroid cancer may go undetected. The following symptoms, however, could appear as the cancer worsens in some people:
– A painless lump grows in the neck below Adam’s apple.
– Thyroid cancer can change the voice, making it hoarse.
– If the lump gets bigger, it presses on the breathing tube, making swallowing hard and painful.
– A growing lump in the throat can cause neck, jaw, or ear pain.
– The cancerous cells might make nearby nodes bigger and easier to feel.
– Big lumps can make it hard to breathe, especially when lying down.
– Some might have a long-lasting cough that doesn’t go away with normal treatments.
– Tiredness has many causes; some people with thyroid cancer might feel very tired without a clear cause.
The Risk Factors of Thyroid Cancer
Regarding understanding the risk factors for thyroid cancer, it’s true that many uncertainties exist. However, there are certain identifiable risk factors that play a crucial role in both recognizing thyroid cancer early and potentially preventing its progression.
This proactive approach not only increases the likelihood of successful outcomes but also contributes to lowering the risk of mortality in this disease.
Some of the common risk factors for thyroid cancer include:
– Gender: Thyroid cancer is very common in women than in men. The reason is that women experience more hormonal changes than men do, including menstruation, pregnancy, and other factors that have a significant impact on the development of thyroid cancer.
– Age: Although thyroid cancer can develop at any age, it is typically detected in patients between the ages of 25 and 65.
– Family history: Having a first-degree relative (parent, sibling, or child) who has thyroid cancer or other related diseases like familial medullary thyroid cancer syndrome or multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) syndromes can increase the risk.
– Radiation Exposure: Thyroid cancer risk is increased by high radiation exposure, particularly in early life. This might be the result of things like radiation treatment for other cancers, nuclear accidents, or specific medical procedures.
– Personal History of Thyroid Disease: People who have a history of certain thyroid conditions, such as goiter (enlarged thyroid) or thyroid nodules, may be at a slightly higher risk.
– Iodine Levels: Iodine is required for thyroid hormone production. Both lower and higher intakes of iodine in diets have a higher thyroid cancer risk.
– Obesity: According to some studies, obesity raises the risk of thyroid cancer, especially the more aggressive forms.
– Diet: If your diet is rich in processed foods and low in fruits and vegetables, carried a slight risk of causing this disease.
The Treatment Options for Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer treatment depends on cancer type, stage, and health. Here are the key options for treating thyroid cancer :
Surgery
Lobectomy: A lobectomy is a surgery that removes the part of the thyroid lobe with cancer, often with the isthmus (a bridge between the lobes). It’s mostly used to treat small papillary or follicular thyroid cancers that haven’t spread beyond the thyroid.
Thyroidectomy: It is the standard surgical treatment for the majority of thyroid cancers. It entails removing a portion or all from thyroid gland and any affected lymph nodes in the neck.
Lymph Node Dissection: A lymph node dissection is performed in some cases, particularly when cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Radioactive Iodine Therapy
Some thyroid cancer cell types, such as thyroid remnants or metastases, may still exist in the body after a thyroidectomy. Radioactive iodine (RAI) can treat thyroid cancer by targeting thyroid cells.
The thyroid is the organ that absorbs the majority of it, and it kills any thyroid or cancer cells there may be. This increases the life expectancy of people with papillary or follicular thyroid cancer. However, the benefits of RAI are less certain if the cancer is small and can be removed surgically.
External Beam Radiation Therapy
External beam radiation therapy uses high-energy rays (X-rays) to kill or slow cancer cells. It’s often for medullary and anaplastic thyroid cancer or when iodine therapy isn’t working effectively.
It’s used when cancer has spread beyond the thyroid. Treatments are painless and given several times a week for a few weeks. Setup takes more time than the actual treatment.
Targeted Drug Therapy
Targeted drug therapy is a precise treatment that focuses on cancer growth signals. It’s used for advanced thyroid cancer when other methods don’t work.
Kinase inhibitors like lenvatinib and sorafenib interfere with cancer cell growth signals. They slow down growth and can improve survival. Not all cases use this therapy; doctors decide based on cancer type, stage, and health.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses strong drugs given through the veins or mouth. It’s systemic, flowing through the body to kill cancer cells. For thyroid cancer, chemo isn’t commonly used, except for aggressive types or when other treatments stop working.
Overall, The greater your chance of survival, the earlier thyroid cancer is discovered.
Final Words
Do not worry if you have found thyroid cancer; your fighting spirit will help you get through it.
Just keep doing regular check-ups and open communication with your thyroid doctor about any worries is crucial for early detection and effective treatment when required.
Read Also
- The Role of Ingredients in Your Skincare: What to Look ForSkincare works best when you understand what goes into the products you use daily. Ingredients form the foundation of every formula and determine how the skin reacts over time. Each cream, cleanser, or serum has its own role, determined by its ingredients. Learning what to look for helps you pick products that help skin and… Read more: The Role of Ingredients in Your Skincare: What to Look For
- Your Guide to Finding a Trusted DentistChoosing the right dentist in Sandgate or your area is crucial for maintaining good oral health and achieving a confident smile. With countless dental practices to choose from, patients may find the task daunting. Data from the American Dental Association indicates that there are over 200,000 practicing dentists in the United States, highlighting the importance… Read more: Your Guide to Finding a Trusted Dentist
- Achieving a Defined, Balanced Facial Contour in SingaporeA well-defined jawline and a gently tapered lower face — commonly referred to as a V-shaped face — is a look many people aspire to. In Singapore’s beauty and aesthetic scene, treatments that help refine facial contours have grown in popularity as more individuals seek subtle, natural enhancements that boost confidence and balance facial features.… Read more: Achieving a Defined, Balanced Facial Contour in Singapore
- The Wellness Blueprint: How Your DNA Holds the AnswerGenetic testing is revolutionizing preventive healthcare by offering insights into individual health risks. By analyzing DNA, these tests provide a personalized health blueprint that can guide lifestyle and medical decisions. This approach, often referred to as DNA wellness testing, helps to optimize health naturally and prevent potential diseases. In recent years, genetic testing has become… Read more: The Wellness Blueprint: How Your DNA Holds the Answer
- Exploring the Benefits of Infusion Therapy in OKC: The Ultimate GuideUnderstanding Infusion Therapy: A Deep Dive into Its Purpose and Process What exactly is Infusion Therapy? Infusion therapy is an advanced medical treatment that delivers medication and nutrients directly into the bloodstream through a vein, typically via an IV (intravenous) line. This method is particularly beneficial for patients who require a concentrated dose of medication,… Read more: Exploring the Benefits of Infusion Therapy in OKC: The Ultimate Guide