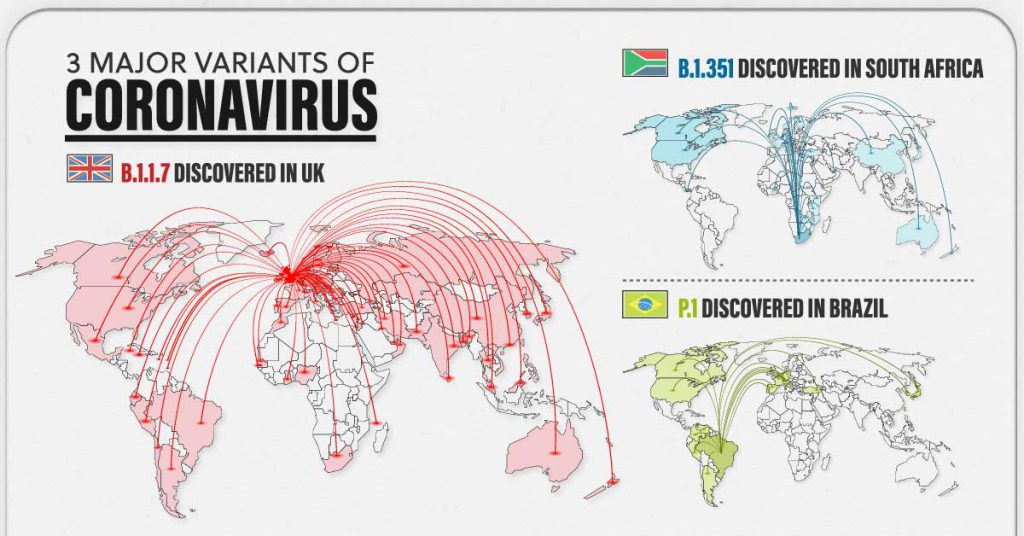
The technical director of the Corona Pandemic Emergency Program at the World Health Organization, Maria Van Kerhove, said that the world is currently facing three mutated strains of the virus, and Kirov indicated that the two strains that were discovered in the UK and South Africa are witnessing a rapid spread, the third variant was discovered in Brazil
The World Health Organization (WHO) and its partners are currently tracking three strains of the virus, which are worrying mutations spreading around the world.
The first strain appeared for the first time in the United Kingdom. B.1.1.7, the second strain appeared for the first time in South Africa. It is B.1.351, as for the third strain, it is P.1 which appeared in Brazil, and it was also discovered among travellers who arrived in Japan.
WHO follows the mutated virus strains and the changes that occur to it and their effect on its ability to spread or affect treatments and vaccines.
Mean so far, statistics confirms that there is an increase in the rapid proliferation of the two strains B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 and this caused by a change in the virus that increased its ability to bind to human cells.
It became known that these new strains are spreading at a faster speed than the first strain that appeared with the Coronavirus, but what is the most dangerous of them? Is it more dangerous than the virus when it appeared more than a year ago?
According to the information and studies available, which confirmed that there is no greater risk, the same mortality rate among those infected with the new strain is still similar to the death rate of the first strain and complications. Therefore until now, there is no clear evidence that the new strains cause more severe diseases.
The good news also must be mentioned, that a decrease noticed in the number of cases worldwide during the last eight weeks, despite the presence of these strains. Therefore we must know the preventive measures, whether the vaccine or other simple social distancing measures or wearing a mask, can reduce the spread of coronavirus disease and viruses, including even new strains.
Is the Coronavirus eligible to develop into other, more new strains?
In fact, the three strains referred to in the report and mentioned by Dr. Maria of the World Health Organization are not the only mutations that occurred to the virus. Thousands of mutations have been monitored, but all of them were simple mutations. The three mutations are the major mutations that have relatively changed the behavior of the virus.
Are we expecting more coronavirus mutations to occur?
Of course, no one knows the virus, as all viruses have the ability to mutate whenever they are transmitted from person to person in most cases, especially viruses of the Corona family, mutations are simple mutations, but it may happen that the change in a vital protein results in a strain with different characteristics, and therefore this cannot be confirmed or denied.
But everyone is linked to the speed of its spread or the greater the spread, the less precautionary measures are taken, the greater the number and percentages of mutations that may come, one of which is a good mutation and mutation in the behavior of the virus.
Can we expect Coronavirus behavior after mutation?
The truth is, of course not, there is no mutation in one direction. The mutation in all directions. The virus consists of tens of thousands of proteins. Each protein remains responsible for a specific behavior of the virus, including the severity of infection, spread, its response to treatments and its response to vaccines in which changes always occur in a very small number of these proteins.
These mutations might not cause changes to the general characters of the virus, but a change may occur, either negatively or positively, of course, according to the protein that has been changed or mutated. Therefore, it is not possible to know in which direction the next mutation will be.
Should we always develop vaccines, or the present enough?
According to so far, there is no need to develop new vaccines, but of course, if there are new strains that do not respond to the current vaccines, of course, we will need to develop vaccines. We may need additional doses, as happens in influenza seasonal vaccines.
The more our preventive measures increase, the less transmission of the virus, the less chance of our other virus mutating. At the stage of its entry into a new organism, it mutates into a new host. It begins to change from itself for reproduction to increase its number, and consequently the fewer the number of infected people, the fewer the chances of mutation.
Again, it’s very important to know that the whole Corona family is a family of stable families. The mutations form simple mutations, and relatively slow, and therefore it is expected that the effectiveness of the current vaccines will last for a longer period.
Does herd immunity reduce the risk of this mutation and these mutated strains?
Absolutely, herd immunity reduces the chances of virus transmission, so most of society keeps immunity. Even the person without immunity does not find someone to infect with the virus. Therefore, the chances of transmission of the disease are minimal.
Therefore, the chances of the virus mutations are reduced. This is what we hope to reach herd immunity as soon as possible through vaccinations, and until we reach this level of immunity, we must once again adhere to the preventive measures that we all must abide by, whether states or individuals.
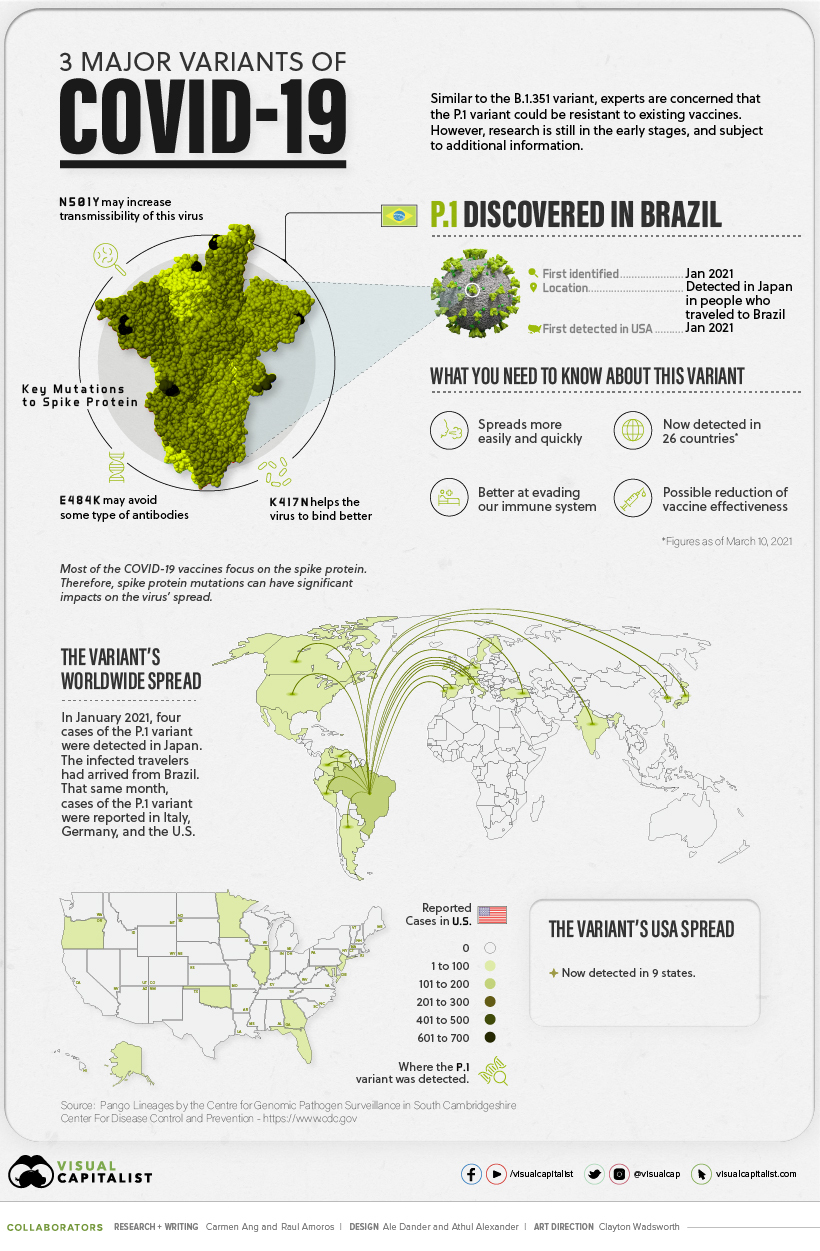
More information about the UK B.1.1.7 coronavirus variant is outlined in the below infographic
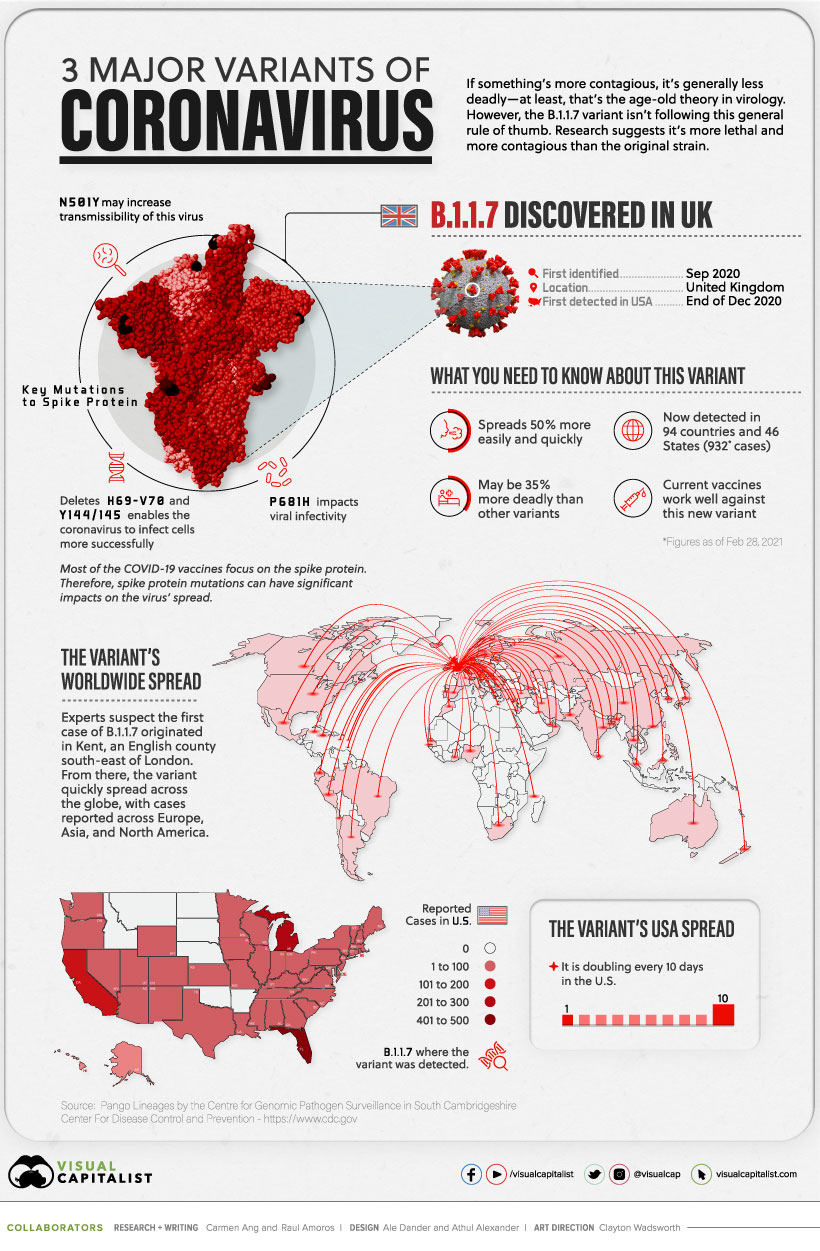
More information about the South Africa B.1.351 coronavirus variant is outlined in the below infographic
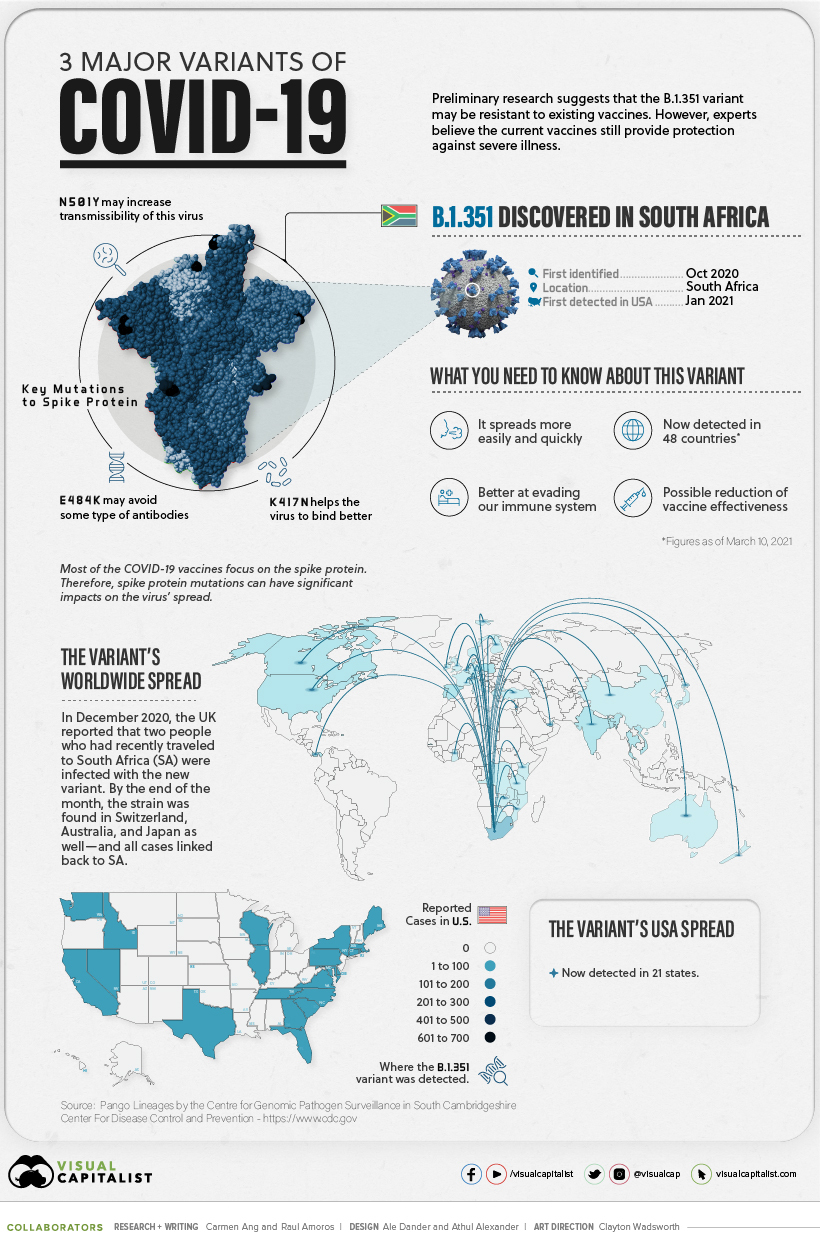
More information about the Brazil P.1 coronavirus variant is outlined in the below infographic