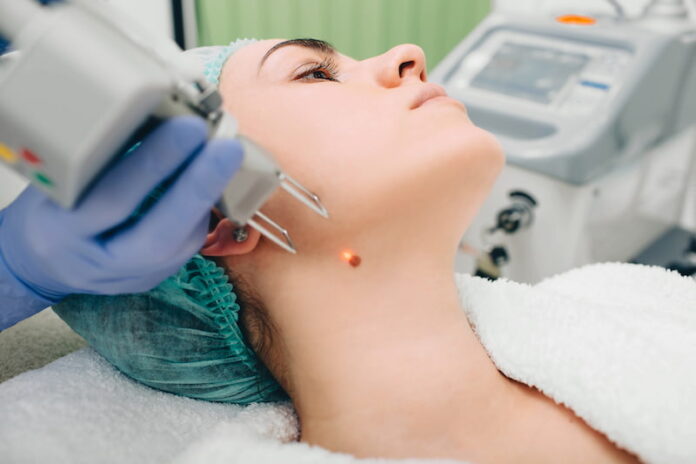
Moles are common skin growths that are usually harmless. However, some moles can be a cause for concern, especially if they change in size, shape, or color. In some cases, moles may need to be removed for medical or cosmetic reasons. This is where dermatologists come in.
Understanding Moles
Moles are growths on the skin that are usually brown or black in color. They can appear anywhere on the body and can vary in size and shape. Most moles are benign and harmless, but some may be atypical or dysplastic, which means they have a higher risk of becoming cancerous.
Appearance and Types of Moles
Moles can appear in different shapes, sizes, and colors. They can be flat or raised, smooth or rough, and may have hair growing from them. The most common types of moles are:
– Junctional moles: These are usually brown and appear on the surface of the skin.
– Compound moles: These are raised and have a darker center.
– Dermal moles: These are flesh-colored or pink and usually raised.
Atypical moles, also known as dysplastic nevus, are moles that have an irregular shape, color, and border. They can be larger than regular moles and have an increased risk of developing into melanoma, a type of skin cancer.
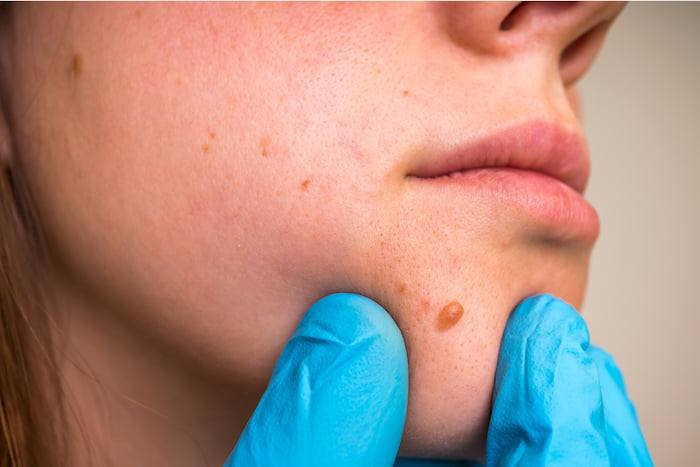
Causes of Moles
Moles are caused by the clustering of melanocytes, which are cells that produce pigment in the skin. They can be present at birth or develop later in life, usually before the age of 30. The number of moles a person has can be influenced by genetics, sun exposure, and hormonal changes.
While most moles are benign and harmless, it is important to monitor them for any changes in size, shape, or color. If a mole looks suspicious or atypical, it is recommended to refer the patient to a dermatologist for further evaluation and possible removal.
Mole Removal Procedures
When a patient has a mole that needs to be removed, there are several procedures that a dermatologist may use. The two most common procedures are shave biopsy and punch biopsy.
Shave Biopsy
A shave biopsy is a procedure that involves using a scalpel or razor blade to shave off the mole. This procedure is typically used for moles that are raised above the skin and do not have any suspicious features. The dermatologist will numb the area with a local anesthetic and then use a scalpel or razor blade to carefully shave off the mole. The area will then be cauterized to stop any bleeding and a bandage will be applied. Stitches are usually not needed for this procedure.
Punch Biopsy
A punch biopsy is a procedure that involves using a circular tool to remove a small cylinder of skin that includes the mole. This procedure is typically used for moles that are suspicious or have irregular features. The dermatologist will numb the area with a local anesthetic and then use the punch tool to remove the mole. The area will then be cauterized to stop any bleeding and a bandage will be applied. Stitches may be needed for this procedure.
It is important to note that both procedures are outpatient procedures and can be performed in the dermatologist’s office. The dermatologist will send the mole to a lab for examination under a microscope (biopsy) to determine if it is cancerous. The results of the biopsy will determine if any additional treatment is needed. Finally, the price of the procedure also depends on where the mole is located and whether a shave or excision is needed.
Post-Procedure Care
After a mole removal procedure, it is important to take proper care of the area where the mole was removed to prevent complications and promote healing. This section will cover two important aspects of post-procedure care: scar prevention and treatment and infection prevention.
Scar Prevention and Treatment
Mole removal can leave a scar, but there are steps patients can take to minimize scarring. The following are some scar prevention and treatment options:
– Keep the area clean and dry to prevent infection and promote healing.
– Apply an antibiotic ointment to the area to prevent infection.
– Avoid exposing the area to sunlight until it has fully healed. Sun exposure can cause hyperpigmentation and make scars more noticeable.
– Apply silicone gel or sheets to the area to help reduce scarring.
– Massage the area gently to promote blood flow and collagen production, which can help reduce scarring.
– Consider using makeup to cover the scar once it has fully healed.
It is important to note that not all scars can be completely prevented or treated. However, taking these steps can help reduce the appearance of scars and promote healing.
Infection Prevention
Infection is a potential complication after mole removal. Patients should take the following steps to prevent infection:
– Keep the area clean and dry.
– Follow the dermatologist’s instructions for wound care.
– Avoid touching the area with unwashed hands.
– Avoid swimming or soaking in water until the area has fully healed.
– Avoid wearing tight clothing that can rub against the area.
If a patient notices signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge, they should contact their dermatologist immediately. In some cases, antibiotics may be necessary to treat the infection.
When to Refer Patients to Dermatologists
Dermatologists are medical doctors who specialize in skin health. They are trained to diagnose and treat various skin conditions, including moles. Patients should be referred to dermatologists for mole removal procedures, signs of skin cancer, and atypical or suspicious moles.
For the Mole Removal Procedure
When patients have moles that are causing discomfort or are aesthetically displeasing, they may opt to have them removed. A dermatologist can perform a mole removal procedure to remove the mole from the skin. This procedure involves shaving or cutting the mole from the skin. After the procedure, the skin will heal, and the mole will be gone.
Signs of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is a malignant growth on the skin that can be caused by excessive exposure to the sun or other factors. Dermatologists are trained to detect the signs of skin cancer and can perform skin cancer screenings to detect any cancerous growths. Patients should be referred to dermatologists if they have any symptoms of skin cancer, such as a mole that is growing in size, has irregular borders, or is not symmetrical in appearance.
Atypical or Suspicious Moles
Atypical moles are moles that have an unusual appearance, color, diameter, or border. These moles may be benign, but they can also be a sign of skin cancer. Dermatologists can perform a biopsy on atypical moles to determine if they are cancerous. Patients with atypical or suspicious moles should be referred to dermatologists for further evaluation.
In conclusion, patients should be referred to dermatologists for mole removal procedures, signs of skin cancer, and atypical or suspicious moles. Dermatologists are trained to diagnose and treat various skin conditions and can provide the necessary care to ensure the health and well-being of their patients.
Read Also
- Why comprehensive health insurance with maternity is beneficial in the UAEWelcoming a child is a significant milestone in any family’s journey. As exciting as this chapter is, it also brings with it a fair share of responsibilities—especially when it comes to planning for healthcare costs. Health insurance is now mandatory in the UAE, but as with any type of insurance, the smallest requirement might not… Read more: Why comprehensive health insurance with maternity is beneficial in the UAE
- Modern Approaches to Adolescent Mental Health Treatment for Lasting RecoveryWith increasing numbers of teens experiencing emotional and behavioral health concerns, adolescent mental health treatment has become more essential than ever. Conditions such as anxiety, depression, trauma and mood instability are on the rise, and effective support must evolve with these growing needs. Today’s treatment models blend evidence-based therapy with flexible access and holistic care, giving… Read more: Modern Approaches to Adolescent Mental Health Treatment for Lasting Recovery
- How to Find a 5-Star Dentist Near YouChoosing a dentist is more than just finding someone who can clean your teeth. It’s about selecting a trusted partner in your long-term oral health. A 5-star dentist not only provides excellent clinical care but also delivers a positive patient experience, from the moment you walk in until the moment you leave. Whether you’re new… Read more: How to Find a 5-Star Dentist Near You
- Your Easy-Peasy Guide to Brewing Amazing MatchaHey there! So, you’ve heard all the buzz about matcha – that vibrant green powder that’s not just pretty but packed with good stuff? It can seem a little fancy and intimidating at first, but trust me, making a delicious cup at home is simpler than you think. Forget complicated ceremonies for now; let’s just… Read more: Your Easy-Peasy Guide to Brewing Amazing Matcha
- Embracing Holistic Wellness: Insights from a Lansing, MI Health CenterReframing Health: Moving Beyond Symptom Management Treating only symptoms often offers quick relief, yet long-term results stay out of reach. When care zeroes in on isolated complaints, the bigger picture, such as stress, behavior, or lifestyle, often gets missed. Research shows that whole-person care, which looks at physical, emotional, and environmental factors, yields better outcomes… Read more: Embracing Holistic Wellness: Insights from a Lansing, MI Health Center