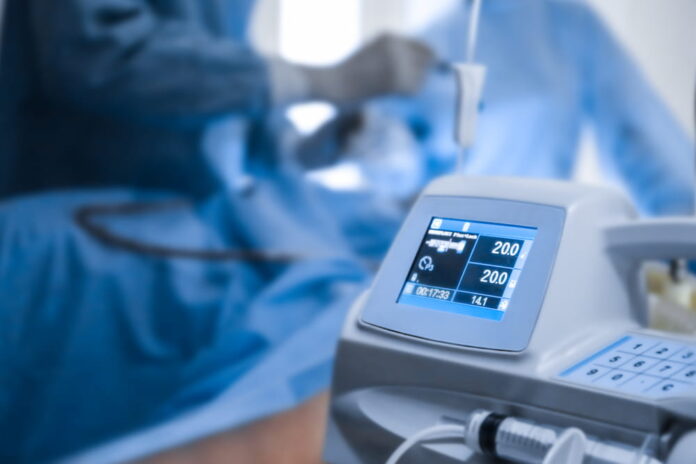
The miniaturization of infusion pumps marked a turning point in healthcare. Without needing to see a doctor, a patient can get precisely measured and scheduled amounts of medication without disrupting their daily lives. Insulin, nutritional supplements, and anticancer medications can now be delivered via mobile pumps.
Pumps, like those from KNF USA and other manufacturers, must be dependable. As a result, it is crucial to think about the components such as the pump itself, the motor, the driver, and the feedback throughout the design phase. They must all meet specifications for ease of use and functionality.
Important Factors To Think About When Choosing A Medical Pump
Inexperienced medical equipment designers may focus solely on pressure and flow rate when choosing a pump. While this may be true for some commercial uses, the standards for medical equipment are different. To guarantee that the proper medical pump is selected for every application, it is necessary to consider the following criteria.

1- The Amount Of Fluid It Can Hold
Medical pumps come in various sizes to accommodate a wide range of needs. A pump’s maximum permitted size and power consumption depend heavily on its intended function.
Healthcare equipment is increasingly being moved out of the ward and into homes. Also, instruments are now required to perform a greater number of tests inside a smaller space. In light of this, these tools’ sizes and power capacities must meet the latest standards.
2- Inlet And Outlet Valves
Aside from the pump, inlet and outlet valves are also important to consider.
It is recommended to select valves and tubing together to ensure that all parameters (such as volume, flow rate, pressure capability, and chemical compatibility) are met.
Specificity also matters. Simple check valves can be employed in certain circumstances. Meanwhile, solenoid valves that are actively regulated may be preferable when high performance is necessary for a system.
The rate and precision of the dispensing are directly related to the quality of the inlet and exit valves. When the pump raises the system pressure to an unsafe level, the valves must open reliably and rapidly to prevent damage. They also need to be able to close quickly enough to stop the flow properly when necessary.
3- Distribution Traits
It is important to think about a wide range of dispensing criteria when choosing the best pump for your application.
The smallest volume that may be dispensed by a pump controlled by a stepper motor is an example of its dispense resolution. Resolution is a function of several variables, including piston diameter, lead screw pitch, and stepper motor angle per step.
To move the piston in and out, most reciprocating pumps rely on a stepper motor turning a lead screw. Microstepping the motor, which divides the step angle by a smaller number, allows for even finer adjustments to the resolution.
Thanks to higher resolution, dispensing increments can be made much smaller, and flow throughout a given dispensing cycle can stay constant.
4- Tubing Size
Another common source of trouble is incorrectly sized tubing. Excessively narrow exit tubing can cause unwanted pressure fluctuations. Because a positive displacement pump may boost pressure in the system, it can be used to overcome resistance further down the line.
If the resistance is too great, the dispensing speed may need to be slowed down, or the tubing diameter may need to be increased. Failures like system leakage and motor stalling might occur without proper maintenance.
5- Fluid Compatibility
Material compatibility within your system is also crucial. A mismatch between the pump’s wetted materials and the system fluid is a leading cause of premature pump failure.
After a flow circuit has been designed, the fluid’s compatibility with the system’s materials must be evaluated. Pumps, valves, manifolds, and piping are part of this system.
Even though some fluids may not chemically harm a pump, they might still cause physical damage. Crystals in fluids used in reciprocating pumps can degrade seals and cause leakage. Likewise, surfactants reduce surface tension, allowing other fluids to bypass the pump’s seals. These problems could be alleviated by using a secondary seal with the pump. To prolong the device’s cycle life, an intermediate fluid is pumped between the seals to dissolve crystals and dilute surfactants.
The Bottom Line
The incorrect pump can cause delays in processing. The end goal must be understood thoroughly before an appropriate pump can be selected.
Make sure to factor in these things when choosing pumps to be used for medical equipment: their fluid capacity, the valves, tubing size, distribution, and fluid compatibility. This way, you can consistently provide quality products for patients who rely on them to stay healthy and live well.
Read Also
- How to increase your healthcare facility efficiency and productivity for a better ROI in 2021?Success in any organization starts with the management role of driving this organization to success via professional management, healthcare facilities are complex in nature due to the complexity of medical procedures, daily operations and the need for a lot of specialties who provide services that fulfill all patient needs. For a better management of your… Read more: How to increase your healthcare facility efficiency and productivity for a better ROI in 2021?
- What are the new capabilities of 640 Slice Ct Scanners?Technology has no end in every single field, medical imaging is one of the areas that has biggest space for development. Over the past decade, computed tomography manufacturers have adopted different approaches to improving scanner performance. Many of these developments have focused on heart CT scans, but the increased use of CT scans has also… Read more: What are the new capabilities of 640 Slice Ct Scanners?
- What is a PACS solution (Picture Archiving and Communication System?PACS is an abbreviation that stands for Picture Archiving and Communication System, healthcare professionals in the Middle East and Africa call it PACS system or PACS solution. It’s one of medical imaging technology that transforms the conventional paper workflow of radiology images and reports into a paperless workflow, it’s mainly responsible for Receiving, storing and… Read more: What is a PACS solution (Picture Archiving and Communication System?
- Discover the top 3 keys of healthcare marketing successDo you want your healthcare marketing to take off and get much more of your ideal new patients, let us go over the three keys of marketing success for healthcare providers, no matter how your prospective patient had heard about you, insurance listing you cover, recommendation by your existing patients, referred by other physicians, or… Read more: Discover the top 3 keys of healthcare marketing success
- Discover the revolutionary Healthcare trends in 2021The mark of the new year is an exciting time, and if you looked at any training healthcare statistics from the past decade, you’d notice that many of them make projections to the next decade, they all did this because 2020 is a benchmark year and at the time it sounded so much further away… Read more: Discover the revolutionary Healthcare trends in 2021
- What is the Main Advantage of Interoperability within an Electronic Health Records (EHR) System?Overview Things used to be a little simpler in hospitals, patients had paper charts where doctors and nurses wrote notes. there weren’t quite as many systems collecting data on vitals and beeping about updates. Fast forward to the present, healthcare has become much more complex and care is coordinated by diverse teams, a single patient… Read more: What is the Main Advantage of Interoperability within an Electronic Health Records (EHR) System?
- Top 3 Reasons Patients Don’t Enroll in Clinical Trials WorldwideIf you have been in or near the research industry for any period of time, you know that there is a huge gap between the patients we need and the patients interested in pursuing clinical research.
- Robotic Surgery: History, Advantages, Disadvantages and ApplicationsScience and technology are the engines of development and the most important reason for global prosperity, they almost contribute to every field in the world, and they are working to develop them