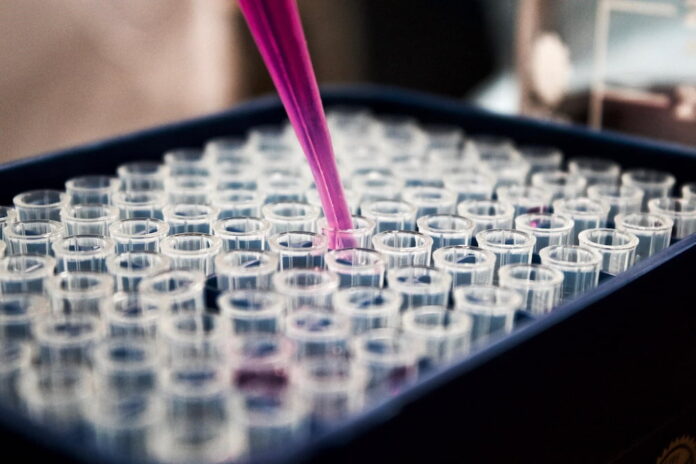
Understanding biochemical and cell-based assays is key to developing relevant and timely drug targets for pharmaceutical companies. These two assays, while related in many ways, are fundamentally different in function.
While both types of assays serve the purpose of drug development and target identification – they differ based on complexity, cost, the scope of applications, the type of results generated, and the accuracy delivered.
In this blog post, we will discuss when it’s appropriate to use biochemistry vs cell-based assays and review their critical differences as vital knowledge for developers engaging in drug discovery activities.
Typical Assay Procedure Steps
To ensure accurate results, the assay process typically requires multiple steps. Prior to each procedure, particularly for cell-based assays, lab staff must confirm that the microplates have been washed in the microplate washer. This step eliminates any leftover residue from previous assays and guarantees clear and precise results for the ongoing assay.
The initial stage towards achieving precise outcomes is to adequately prepare the sample for analysis through homogenization, filtration, or centrifugation. After that, an extractive process is done on the sample to concentrate the analyte of interest and separate it from other compounds that may interfere with its detection. Typically, this process involves chemical or physical techniques like distillation, solvent extraction, and adsorption/desorption.
The third step requires the utilization of methods and techniques to carry out a quantitative assessment and ascertain the analyte’s concentration in the sample. The results are then analyzed to interpret the concentration and determine its significance in relation to a standard or reference material.
Keep in mind that developing a complete assay can take anywhere between 6 to 24 months. Although it may seem like a lengthy process, it allows scientists to obtain precise results and conduct their research accurately.
Biochemical Assays Overview
Biochemical assays are essential tools for detecting and measuring molecules, cells, and biochemical processes in living organisms. Professionals use these assays to detect and study molecules such as proteins, enzymes, and antibodies. This enables a better understanding of cell function, disease development, and drug action. Biochemical assays are crucial for advancing our knowledge of biology in both laboratory and field settings.
Biochemical Assays Pros and Cons
Scientists use biochemical assays as powerful tools to study various biological processes. The assays are advantageous because they are highly sensitive, enabling the detection of specific molecules, even at very low levels in complex biological samples.
Although biochemical assays are beneficial, they also have some limitations. They tend to consume a lot of time and need specialized know-how. Furthermore, there could be inconsistencies in the findings due to diverse experimental conditions. Nonetheless, researchers in different areas find biochemical assays a precious resource.
Cell-Based Assays Overview
Modern biomedical research relies heavily on cell-based assays as they provide a controlled environment for scientists to observe cellular interactions and processes. These assays involve using live cells to investigate how cellular behavior is affected by stimuli such as toxins, drugs, and environmental factors.
Advanced imaging technologies and high-throughput screening techniques enable scientists to delve deeper into cell growth, morphology, and gene expression, yielding vital information on disease mechanisms and the discovery of novel drug targets. Because of these advancements, cell-based assays have become increasingly complex. As a result, they are now an essential part of drug discovery and other biomedical research fields, providing valuable information about how cells operate.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cell-Based Assays
Scientists use cell-based assays to explore biological systems, diseases, and treatments. These assays are more accurate than traditional tests in showing how drugs work in the human body. That’s why they are particularly useful in research. Additionally, they can be used to examine intricate biological pathways and identify potential drug targets.
Even though cell-based assays are advantageous, there are certain downsides that need consideration like their higher cost, longer development period, and the need for specialized equipment and expertise.
Bottom Line
Biochemical assays and cell-based assays are both valuable laboratory methods. Determining the suitability of an assay is crucial for a research project. Biochemical assays provide data analysis that is quick and simple, while cell-based assays offer valuable information on how a system behaves in its natural surroundings. The choice of assay will vary depending on the nature of the research and the researcher’s available resources. Scientists should carefully consider all options to select the best experiment for their lab work.
Read Also
- Optimizing CT Protocols: The Hidden Key to Efficiency and Cost Savings in RadiologyIntroduction: Why CT Protocol Optimization Matters Computed Tomography (CT) is a cornerstone of modern diagnostic imaging, providing critical information across nearly every medical specialty. However, maximizing the value of CT — both clinically and financially — requires more than just advanced hardware. The real secret lies in the optimization of CT protocols. When CT protocols… Read more: Optimizing CT Protocols: The Hidden Key to Efficiency and Cost Savings in Radiology
- The Role of Carbide Burs in Modern Dental ProceduresAs a result of this procedures need to be well coordinated and to this end, precision tools are used by dental practitioners. Among the most essential tools in a dentist’s arsenal are carbide burs, which have revolutionized various aspects of dental work. Today’s dentistry cannot work without these tools as they are both strong, sharp,… Read more: The Role of Carbide Burs in Modern Dental Procedures
- Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy: The AI AdvantageDiabetic retinopathy (DR) is a leading cause of blindness among working-age adults, affecting millions worldwide. The prevalence of DR is alarmingly high, affecting an estimated 34.6 million people globally. In the United States alone, it is estimated that 7.7 million adults have some form of diabetic retinopathy. How Does Diabetes Affect the Eye? Most of… Read more: Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy: The AI Advantage
- Advances in Digital Health: Transforming Modern HealthcareThe healthcare landscape is undergoing a seismic shift with the advent of digital health technologies. These innovations are not just modern conveniences; they are transformative tools that bridge gaps in accessibility, improve patient outcomes, and empower individuals to take charge of their health. From wearable devices to telehealth and artificial intelligence, digital health is creating… Read more: Advances in Digital Health: Transforming Modern Healthcare
- The Latest Advancements in Urology ProceduresUrology, the branch of medicine concerning the urinary system and male reproductive organs, has seen remarkable advancements in recent years. Technological innovations have led to more precise, less invasive, and increasingly successful procedures that promise better outcomes for patients. From state-of-the-art robotics to personalized medicine approaches, the field of urology is evolving at a rapid… Read more: The Latest Advancements in Urology Procedures
- Navigating the Future of Healthcare: The Role of Technology and Innovation at Saint Luke’s HospitalIn an era of rapid technological advancement, the landscape of healthcare is undergoing a profound transformation. At the forefront of this evolution is Saint Luke’s Hospital, a leading medical institution in Los Cabos, Mexico. With a commitment to providing cutting-edge care to its patients, the hospital is harnessing the power of technology and innovation to… Read more: Navigating the Future of Healthcare: The Role of Technology and Innovation at Saint Luke’s Hospital