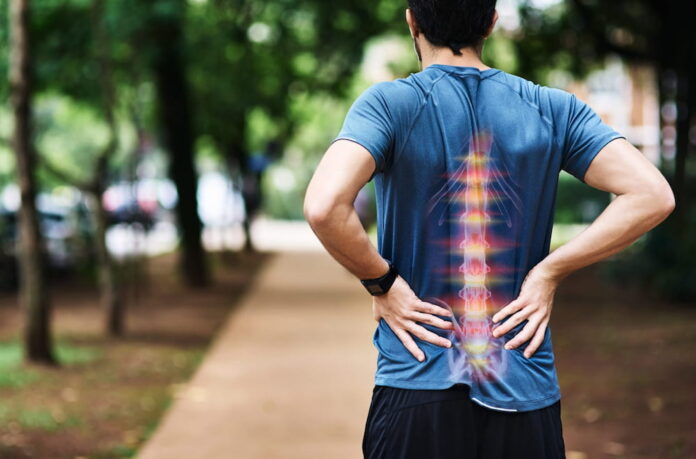
Back pain is a pervasive and often debilitating condition affecting millions globally. One of the common culprits behind chronic back pain is disc herniation. This condition, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, can result in significant discomfort and restricted mobility. Understanding the nature of disc herniation and effective treatment strategies is crucial for managing this condition and improving quality of life.
While traditional treatments for disc herniation include physical therapy, medications, and sometimes surgery, innovative therapies are emerging as potential game-changers. One such advanced treatment is Discseel, a minimally invasive procedure that aims to repair and seal damaged discs using fibrin, a natural protein used by the body in the clotting process. This method not only alleviates pain but also helps in the regeneration of disc tissue, making it a promising option for those suffering from herniated discs.
Discseel offers numerous benefits over conventional surgical procedures. It typically involves a shorter recovery time, reduced risk of complications, and less postoperative pain. Moreover, it addresses the root cause of disc herniation by promoting the healing of the torn annulus fibrosus, potentially providing long-term relief and improved spinal health.
Given the debilitating nature of disc herniation, exploring all available treatment options, including innovative ones like Discseel, becomes essential. Patients and healthcare providers can work together to develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to individual needs, enhancing the chances of a successful recovery and a better quality of life.
What is Disc Herniation?
The spine comprises a series of bones (vertebrae) cushioned by intervertebral discs. These discs act as shock absorbers, providing flexibility and support to the spine. Each disc has a tough exterior (annulus fibrosus) and a soft, gel-like center (nucleus pulposus). Disc herniation occurs when there is a tear in the annulus fibrosus, allowing the nucleus pulposus to protrude. This protrusion can press on nearby nerves, leading to pain, numbness, and weakness.
Disc herniation often results from age-related wear and tear, known as degenerative disc disease, although it can also be caused by physical trauma or improper lifting techniques. Individuals experiencing this condition may notice symptoms including localized back pain, sciatica, and muscle weakness, which can severely impact daily activities and overall quality of life.
An effective and innovative treatment option to consider is Discseel, which utilizes fibrin to repair and seal damaged discs, promoting natural healing and reducing the likelihood of recurrence. By addressing the root cause of the herniation, Discseel offers a less invasive and potentially more effective alternative to traditional surgical procedures. Understanding these treatment options is crucial for anyone suffering from disc herniation, emphasizing the importance of consulting healthcare professionals to develop a tailored treatment plan. This approach can significantly enhance recovery outcomes, enabling a return to normalcy and pain-free living.
Symptoms of Disc Herniation
The symptoms of disc herniation vary depending on the disc’s location and the severity of the nerve impingement. Common symptoms include:
– Localized Back Pain: The most prevalent symptom is a sharp or burning pain in the lower back.
– Radiating Pain: Pain may extend to other parts of the body, such as the buttocks, legs, or arms, known as sciatica when it affects the sciatic nerve.
– Numbness and Tingling: A herniated disc might cause a tingling sensation or numbness in the areas served by the affected nerves.
– Muscle Weakness: The muscles serviced by the compressed nerves may weaken, potentially impairing the ability to lift or hold objects.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of disc herniation:
– Age: Age-related wear and tear (degenerative disc disease) can make the discs more susceptible to protrusion.
– Trauma: Injuries resulting from lifting heavy objects incorrectly or sudden impact can cause herniation.
– Genetics: A family history of disc herniation can increase individual susceptibility.
– Lifestyle: A sedentary lifestyle, obesity, and smoking can compromise disc health.
Diagnosing Disc Herniation
A thorough medical examination is essential for diagnosing disc herniation. Physicians generally use:
– Medical History and Physical Exam: Initial assessment to understand symptoms and physical signs.
– Imaging Tests: MRI and CT scans provide detailed images of the spine to confirm the diagnosis and locate the herniation.
Treatment Options for Disc Herniation
Treatment for herniated discs ranges from non-invasive methods to surgical interventions, depending on the severity of the condition:
Conservative Treatments
– Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises can strengthen the back muscles, improve mobility, and alleviate pain.
– Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants can help manage symptoms.
– Lifestyle Modifications: Weight loss, ergonomic adjustments, and quitting smoking aid in the treatment process.
Non-Surgical Interventions
– Epidural Steroid Injections: Administering corticosteroids near the affected nerve can reduce inflammation and pain.
– Chiropractic Care: Manual manipulation of the spine by a chiropractor may provide relief for some individuals.
Surgical Options:
Microdiscectomy: A minimally invasive surgery to remove the portion of the disc pressing on the nerve.
Laminectomy: A procedure removing part of the vertebrae to relieve pressure on the nerve roots.
Artificial Disc Replacement: In severe cases, replacing the damaged disc with an artificial one may be necessary.
Preventative Measures
Prevention is key to avoiding herniated discs. Some effective strategies include:
– Regular Exercise: Strengthening core muscles provides better support for the spine.
– Proper Lifting Techniques: Using the legs rather than the back to lift heavy objects minimizes injury risk.
– Ergonomics: Ensuring your workplace setup supports good posture and reduces strain on the spine.
– Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy weight and quitting smoking enhance overall spinal health.
Conclusion
Disc herniation is a challenging condition, but understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options empowers individuals to manage and overcome back pain effectively. Through a combination of conservative treatments, potential medical interventions, and preventive measures, many can find relief and return to a pain-free life. One promising treatment option is Discseel, a minimally invasive procedure that uses fibrin to repair and seal damaged discs. Discseel can provide long-lasting relief by promoting natural healing of the disc tissue while reducing the risk of recurrence.
In addition to innovative treatments like Discseel, it is vital to consult with healthcare professionals who can offer personalized advice and develop the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to each individual’s needs. By being informed and proactive, patients can enhance their quality of life and manage disc herniation more effectively.
Did you find this helpful? Check out our other helpful articles on our website.
Read Also
- Why comprehensive health insurance with maternity is beneficial in the UAEWelcoming a child is a significant milestone in any family’s journey. As exciting as this chapter is, it also brings with it a fair share of responsibilities—especially when it comes to planning for healthcare costs. Health insurance is now mandatory in the UAE, but as with any type of insurance, the smallest requirement might not… Read more: Why comprehensive health insurance with maternity is beneficial in the UAE
- Modern Approaches to Adolescent Mental Health Treatment for Lasting RecoveryWith increasing numbers of teens experiencing emotional and behavioral health concerns, adolescent mental health treatment has become more essential than ever. Conditions such as anxiety, depression, trauma and mood instability are on the rise, and effective support must evolve with these growing needs. Today’s treatment models blend evidence-based therapy with flexible access and holistic care, giving… Read more: Modern Approaches to Adolescent Mental Health Treatment for Lasting Recovery
- How to Find a 5-Star Dentist Near YouChoosing a dentist is more than just finding someone who can clean your teeth. It’s about selecting a trusted partner in your long-term oral health. A 5-star dentist not only provides excellent clinical care but also delivers a positive patient experience, from the moment you walk in until the moment you leave. Whether you’re new… Read more: How to Find a 5-Star Dentist Near You
- Your Easy-Peasy Guide to Brewing Amazing MatchaHey there! So, you’ve heard all the buzz about matcha – that vibrant green powder that’s not just pretty but packed with good stuff? It can seem a little fancy and intimidating at first, but trust me, making a delicious cup at home is simpler than you think. Forget complicated ceremonies for now; let’s just… Read more: Your Easy-Peasy Guide to Brewing Amazing Matcha
- Embracing Holistic Wellness: Insights from a Lansing, MI Health CenterReframing Health: Moving Beyond Symptom Management Treating only symptoms often offers quick relief, yet long-term results stay out of reach. When care zeroes in on isolated complaints, the bigger picture, such as stress, behavior, or lifestyle, often gets missed. Research shows that whole-person care, which looks at physical, emotional, and environmental factors, yields better outcomes… Read more: Embracing Holistic Wellness: Insights from a Lansing, MI Health Center
- VO₂ Max Testing Explained: What It Is & Why It Matters for Your HealthVO₂ max sounds like a term reserved for elite athletes, but it’s among the most accurate measures of your lifetime and general condition. Moreover, it goes beyond performance. Monitoring your VO₂ max will help you to ascertain your body’s capacity to control stress, its oxygen consumption efficiency, and your internal ageing process. If you have… Read more: VO₂ Max Testing Explained: What It Is & Why It Matters for Your Health
- So, what exactly is matcha?Think of matcha as green tea turned up to eleven! Instead of steeping leaves and tossing them out, matcha is made by grinding whole green tea leaves into this super-fine, vibrant green powder. You whisk it right into hot water (or milk!), meaning you’re drinking the entire leaf. That’s why folks say you get way… Read more: So, what exactly is matcha?
- How to Tell When It’s Time for Professional Senior Care SupportCaring for an aging loved one is a journey filled with love, patience, and difficult decisions. One of the toughest choices families face is knowing when it’s time to seek extra help. In this article, trusted Los Angeles caregivers for seniors explore the signs that it might be time to bring in professional support, not… Read more: How to Tell When It’s Time for Professional Senior Care Support